About the Ear and Its Disorders
Home to the organs of hearing and balance
The ear houses the organs of hearing and balance, as well as important cranial nerves such as:
- the facial nerve, which moves the face
- the lower cranial nerves, which coordinate and allow swallowing and speech
- the carotid artery and jugular veins
The ear is divided into the external ear canal, the middle ear and the inner ear—and is connected to the brainstem via the cranial nerves.
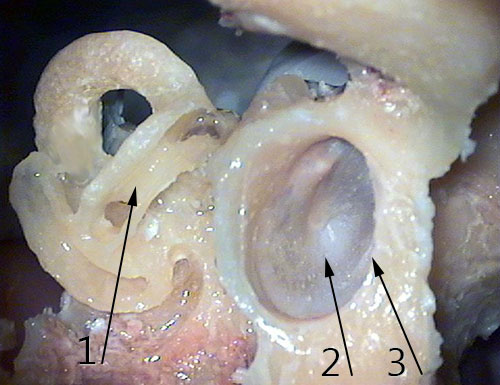
- Semicircular canals
- Tympanic membrane (eardrum)
- External ear
View from superiorly in axial section
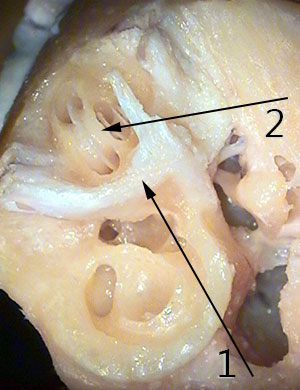
- Facial nerve
- Cochlea
Essentially, the function of the ear is to:
- collect sound (pinna and external ear canal)
- increase sound pressure so that it can drive vibrations in the fluid-filled inner ear (middle ear function)
- convert sound into nerve impulses to the brain (inner ear)
The balance organs serve to sense rotational accelerations (semicircular canals) and linear accelerations, including gravity (saccule and vestibule).
Disorders of the ear
There are many disorders of the ear that manifest in numerous ways. Some common ones, along with common interventions, include:
