Hyo-Sung Ro
Professor

Email: hyo-sung.ro@dal.ca
Phone: 902-494-2367
Phone: 902-494-2301
Mailing Address:
Sir Charles Tupper Medical Building
PO Box 15000
Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada B3H 4R2
Education
- PhD, McMaster University
Academic Positions
- Department member since 1989
Research Topics
Role of chronic inflammation in cancer and metabolic diseases
Research
Signalling mechanisms of chronic inflammation/macrophage activation in atherogenesis, mammary tumorigenesis, and type 2 diabetes mellitus
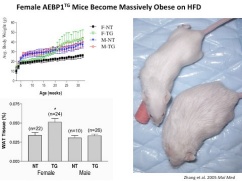
Adipocyte Enhancer-Binding Protein 1 (AEBP1) is a transcriptional repressor that was initially shown to be involved in adipocyte differentiation. Studies with the AEBP1 transgenic mice (AEBP1-TG), which overexpresses AEBP1 transgene in the adipose tissues and macrophages, and the AEBP1 knockout mice (AEBP1-KO) suggested that AEBP1 plays a key functional role in in-vivo modulation of adiposity and energy metabolism.
Project 1 - Role of AEBP1 in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis, foam cell formation, inflammation and atherogenesis
A key event in atherogenesis is foam cell formation, which is mediated by lipid uptake by macrophages. PPARγ1 and LXRα are nuclear receptors that play integral roles in cholesterol efflux and lipid homeostasis. Atherosclerosis is a long-term, inflammatory process involving recruitment and activation of multiple cell types to the intima of the arteries, subsequently leading to a local inflammatory response, which advances atherogenesis due to the sustained recruitment of monocytes/macrophages to the inflamed vasculature. AEBP1 is a transcriptional repressor with a critical role in cholesterol homeostasis, which it impedes macrophage cholesterol efflux and promotes foam cell formation by regulating the expression of cholesterol efflux and pro-inflammatory mediators via PPARγ1 and LXRα repression. AEBP1-TG mice exhibit hyperlipidemia and develop atherosclerotic lesions in their proximal aortae. AEBP1 may be a novel pro-atherogenic factor, and our colonies of AEBP1-TG and AEBP1-KO mice will allow more precise clarification of AEBP1's role in atherogenesis, and establishing a direct link of AEBP1 signaling pathways to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Targeting AEBP1 signaling pathway in the control of inflammation may be useful in the treatment of atherosclerosis.
Project 2 - Role of AEBP1 in regulation of mammary gland development and tumorigenesis via stromal-epithelial crosstalk
A complex interplay between epithelial and stromal compartment of mammary tissue is critical in the control of mammary gland development. The signaling pathways regulating the crosstalk between the mammary epithelium and stroma are also implicated in mammary tumorigenesis. AEBP1 promotes macrophage inflammatory responsiveness via up-regulation of NF-κB activity. Several pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, all of which are encoded by target genes of the NF-κB activation pathway, can promote tumor growth in human and mice. Ablation of AEBP1 causes lactation defect during mammary gland development. Mammary epithelial cell transplantation experiments and stromal restoration of AEBP1 in the AEBP1-KO mice indicated that AEBP1 is a critical stromal factor in mammary gland development. AEBP1-TG mice with targeted AEBP1 over-expression in stroma display spontaneous development of mammary tumors that is preceded by mammary epithelial cell hyperplasia. AEBP1 may be a novel mediator of tumor promotion in the molecular link between inflammation and carcinogenesis. The specific aims are to (1) assess AEBP1's involvement in modulation of stromal-epithelial crosstalk; and (2) define the signaling mechanism(s) of the stromal-epithelial communication in the regulation of mammary gland development and tumorigenesis.
Project 3 - Targeting macrophage infiltration and tissue inflammation to relief of diet- and obesity-induced insulin resistance
Low-grade obesity-induced inflammatory responses play an important role in the etiology of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Recent findings indicate that the inflammatory state, not development of obesity per se, contributes to insulin resistance that contribute to T2D. We will determine whether AEBP1 that regulates adipose tissue metabolism and inflammation, functions as a critical regulator of obesity-induced inflammation in the adipose tissue and liver that predispose toward insulin resistance. Bone marrow transplantation technique has been used to selectively alter macrophage AEBP1 expression in the context of two murine models of obesity, high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice and genetically predisposed obese mice (Ob/Ob). Preliminary analysis indicated that AEBP1 ablation in macrophage markedly normalized glucose tolerance in both HFD-fed and genetically obese mice. Myeloid cell AEBP1-KO mice will be also generated using the Cre-LoxP system. In this way, the promoting function of macrophage inflammatory pathway will be disabled while the expression of AEBP1 remains intact in all other tissues. Understanding the role of AEBP1 in the regulation of inflammatory response in the adipose tissues and liver is crucial for designing strategies to ameliorate T2D.
Keywords:
Transfection, Q-PCR, Bone Marrow Transplantation
Publications
- Majdalawieh, A.F. and Ro, H.-S., (2015) Sesamol and sesame (Sesamum indicum) oil enhance macrophage cholesterol efflux via up-regulation of PPARγ1 and LXRα transcriptional activity in a MAPK-dependent manner. Eur J Nutr 54(5):691-800 [PubMed]
- Majdalawieh, A.F. and Ro, H.-S., (2014) The anti-atherogenic properties of sesamin are mediated via improved macrophage cholesterol efflux through PPARγ1-LXRα and MAPK signaling. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 84(1-2):79-91 [PubMed]
- Holloway, R.W., Bogachev, O., Bharadwaj, A.G., McCluskey, G.D., Majdalawieh, A.F., Zhang, L., and Ro, H.-S., (2012) Stromal adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1 (AEBP1) promotes mammary epithelial cell hyperplasia via proinflammatory and hedgehog signaling J. Biol. Chem. 287:39171-39181 [PubMed]
- Bogachev, O., Pan, X., Majdalawieh, A., Zhang, L. and Ro, H.-S., (2011) Adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1 (AEBP1) (a novel macrophage proinflammatory mediator) overexpression promotes and ablation attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- and LDLR-/- mice. Mol. Med. 17:1056-1064 [PubMed]
- Zhang, L., Reidy, S.P., Bogachev, O., Hall, B.K., Majdalawieh, A. and Ro, H.-S., (2011) Lactation defect with impaired secretory activation in AEBP1-null mice. PLoS One 6(11):e27795 [PubMed]
- Majdalawieh, A. and Ro, H.-S., (2010) Regulation of IkappaBalpha function and NF-kappaB signaling: AEBP1 is a novel proinflammatory mediator in macrophages. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:823821 [PubMed]
- Majdalawieh, A. and Ro, H.-S., (2010) PPARgamma1 and LXRalpha face a new regulator of macrophage cholesterol homeostasis and inflammatory responsiveness, AEBP1. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 8:e004 [PubMed]
- Majdalawieh, A. and Ro, H.-S., (2009) LPS-induced suppression of macrophage cholesterol efflux is mediated by adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41:1518-1525 [PubMed]
- Miller, J.R., Siripurkpong, P., Hawes, J., Majdalawieh, A., Ro, H.-S. and McLeod, R.S., (2008) The trans-10, cis-12 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid decreases adiponectin assembly by PPARγ-dependent and PPARγ-independent mechanisms J. Lipid Res. 49:550-562 [PubMed]
- Ro, H.-S., Zhang, L., Majdalawieh, A., Kim, S.-W., Wu, X., Lyons, P., Webber, C., Ma, H., Reidy, S., Boudreau, A., Miller, J., Mitchell, P. and McLeod, R., (2007) Adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1 modulates adiposity and energy homeostasis. Obesity 15(2):288-302 [PubMed]
- Majdalawieh, A., Zhang, L. and Ro, H.-S., (2007) Adipocyte enhancer-binding protein-1 promotes macrophage inflammatory responsiveness by up-regulating NF- κ B via I κ B α negative regulation Mol. Biol. Cell 18:930-942 [PubMed]
- Majdalawieh, A.F., Zhang, L., Fuki, I.V., Rader, D.J. and Ro, H.-S. , (2006) Adipocyte Enhancer-Binding Protein-1 is a potential novel atherogenic factor involved in macrophage cholesterol homeostasis and inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103 (7):2346-2351 [PubMed]
- Lyons, P.J., Mattatall, N.R. and Ro, H.-S., (2006) Modeling and functional analysis of AEBP1, a transcriptional repressor. Proteins 63:1069-1083 [PubMed]
- Lyons, P.J., Muise, A.M. and Ro, H.-S., (2005) MAPK modulates the DNA binding of adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1. Biochemistry 44:926-931 [PubMed]
- Zhang, L., Reidy, S.P., Nicholson, T.E., Lee, H.-J., Majdalawieh, A., Webber, C., Stewart, B.R., Dolphin, P. and Ro, H.-S., (2005) The role of AEBP1 in sex-specific diet-induced obesity. Mol. Med. 11:39-47 [PubMed]
- Ro, H.-S., (2004) Adipocyte-enhancer binding unit 1 Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes 2nd Edn, A.J. Barrett, N.D. Rawlings and J.F. Woessner (eds.) Academic Press Limited:846-848
- Ro, H.-S., Kim, S.-W., Wu, D., Webber, C., and Nicholson, T.E., (2001) Gene structure and expression of the mouse adipocyte enhancer-binding protein. Gene 280:123-133 [PubMed]
- Kim, S., Muise, A.M., Lyons, P.J., Ro, H.-S., (2001) Regulation of adipogenesis by a transcriptional repressor that modulates MAPK. J. Biol. Chem. 276:10199-10206 [PubMed]
- He, G.-P., Kim, S. and Ro, H.-S., (1999) Cloning and characterization of a novel zinc finger transcriptional repressor. A direct role of the zinc finger motif in repression. J. Biol. Chem. 274:14678-14684 [PubMed]
- Muise, A.M., Ro, H.-S., (1999) Enzymatic characterization of a novel member of the regulatory B-like carboxypeptidase with transcriptional repression function: Stimulation of the enzymatic activity by its target DNA. Biochem. J. 343:341-345 [PubMed]
- Park, J.-G., Muise, A.M., He, G.-P., Kim, S., Ro, H.-S., (1999) Transcriptional regulation by the gamma5 subunit of a heterotrimeric G protein during adipogenesis. EMBO J. 18:4004-4012 [PubMed]
- He, G.-P., Muise, A.M., Wu-Li, A., Ro, H.-S., (1995) A eukaryotic transcriptional repressor with carboxypeptidase activity. Nature 378:92-96 [PubMed]